The Ukrainian War lasted 130 days. More than four months later, Russia changed its strategy, with land, sea and air strikes on most of Ukraine’s territory.
The Russian army is currently focusing its operations on eastern and southern Ukraine, where it has won conquests by using heavy artillery and advancing slowly at key points.
According to President Volodymyr Zelensky, Russian forces currently occupy about 20 percent of Ukrainian territory. That is, 125 thousand square kilometers, including the Crimean peninsula and other areas controlled by pro-Moscow separatists since 2014.
The Armed Conflict Site and Incident Data Project (Acled) has recorded a total of more than 10,000 deaths in Ukraine since the beginning of the conflict. Mariupol (southeast), Kharkiv (northeast) and Bilohorivka (east) recorded the highest death numbers.
Among the latest developments, the following stand out:
- Russian forces took control of the eastern city of Lysychansk;
- Russian troops now control the entire Lugansk region;
- Russian troops withdrew from Snake Island in the Black Sea.
Russia’s last advance is the capture of the nearby city of Severodonetsk.
At the conference held in Lugano, Switzerland on Monday, the 132nd day of the war (4), the “Marshall Plan” was approved for the reconstruction of the country occupied by Russia with an investment of 750 million USD.
(3) On Sunday, several villages were bombed and a secondary school was destroyed in Kharkov.
war map
The area was mapped by the War Studies Institute in the United States with information collected on July 3 and updated on July 4.
Key areas of progress are updated daily by the UK Ministry of Defense and the BBC, but as the situation in Ukraine changes rapidly, there are likely to be changes that are not reflected in the maps.
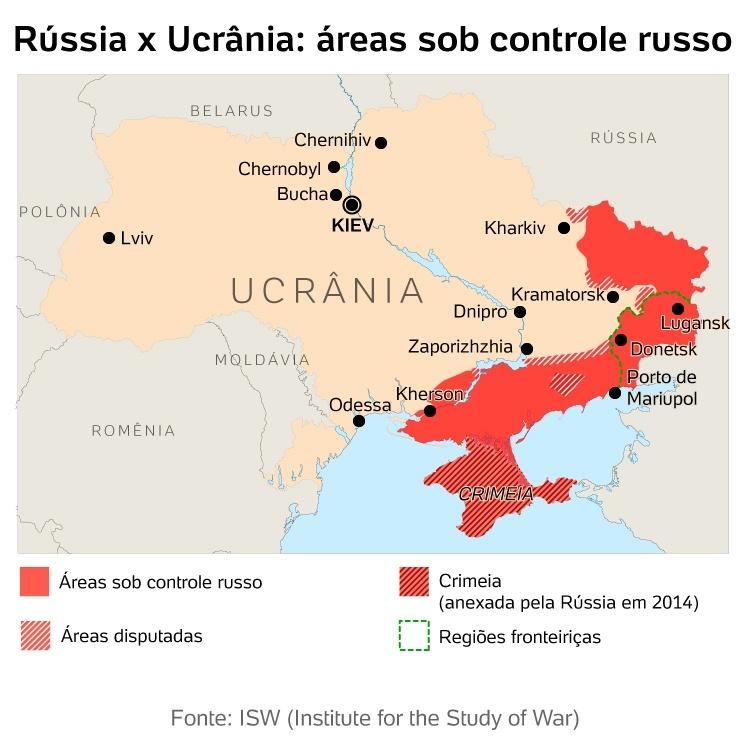
areas under Russian control
- Crimea (annexed by Russia in 2014)
- herson
- Severodonetsk
- luhansk
- Mariupol
- Meltopol
- Donbass
- bed hanger
- New Kakhova
Ukraine regions
- slovyansk
- conotope
- Ternopil
- zaporizhzhia
- Harvik
- Novel
- uzhorod
- khmelnytskyi
- Rivne
- kropyvnytskyi
areas of war
- donetsk
- mycolaiv
- Lysichansk
- Kyiv
- Sumi
- live
- Lutsk
- odessa
- poltava
- Ivano frankivsk
- vinnytsia
- vhytomyr
- dnipro
- Circassian
- Zaporizhia
- Volnovakha
War Chronology
The Russian invasion of Ukraine on February 24 started a full-scale war in Europe. The bet of Russian President Vladimir Putin was a quick victory. But it didn’t.
The first city completely dominated by the Russians was Kherson. On the day that marks a week since the start of the war in Ukraine, Putin’s troops have conquered and already dominated the area near the Zaporizhzhia plant.
On March 13, Russia expanded its war into Western Ukraine, where it launched missiles at a base in Yavoriv.
In a month of war, the United States was preparing for a possible nuclear war. Russia attacked two buildings in Lviv, a city close to the Polish border.
In late March, Moscow signaled that it was reducing its ambitions and would focus on territory claimed by Russian-backed separatists in the east, while Ukrainian forces went on the offensive to retake cities outside of Kyiv.
April
On April 1, Ukraine recaptured another territory around Kyiv with villages destroyed by Russian soldiers. In the days that followed, the country accused Russia of war crimes, including the missile attack on a train station in Kramatorsk.
According to Ukraine, Russia’s main warship in the Black Sea, Moskva, sank on the 14th after an explosion and fire caused by a missile strike. Four days later, Russia launched its offensive in the east of the country.
On April 21, President Vladimir Putin declared victory in Mariupol, but clashes were still reported in the city. On April 25, Russia claimed to bomb Ukrainian military installations and the Kremenchuk Oil Refinery.
May
Local officials in the Odessa region said Russian missiles hit a bridge crossing the Dniester estuary.
According to reports from the Ukrainian Armed Forces, the Russians occupied the east, while the country’s soldiers attacked in the south.
Luhansk Governor Serhiy Haidai reported that Russia bombed a school in the Bilohorivka region, two people were killed and 60 people were injured. For example, on May 9, ballistic missiles hit a shopping mall and two hotels.
According to local authorities, on May 14, Russian troops withdrew from the Kharkov region after successful counterattacks by the Ukrainian army.
On the 20th, Russian missiles hit the Palace of Culture in the city of Lozova in the Kharkov region. On May 25, it was reported that the city of Svitlodarsk in the north of Ukraine’s Donetsk Oblast was conquered by the Russians. The struggle for the city of Severodonetsk continued until the end of the month.
June
On June 5, Ukraine claimed to have killed the commander of the Russian 29th Combined Arms Army, Lieutenant General Roman Berdnikov, according to information confirmed by Russian television.
In the middle of the month, Luhansk’s Ukrainian governor, Serhiy Haidai, confirmed that Ukrainian army units were stranded in Severodonetsk after the Russians blew up bridges. Meanwhile, the Russian army followed with powerful weapons.
On June 19, the Russian Ministry of Defense claimed that it had hit a Ukrainian command post near the city of Dnipro with several Kalib cruise missiles. Then Serhiy Haidai confirmed that Russian troops had captured the city of Metiolkine.
On June 24, Ukrainian forces were ordered to withdraw from the city of Severodonetsk. On the night of June 25, Russian missiles were fired at military installations in Lviv, Zhitomir and Chernihiv regions.
The Russians withdrew from Kobra Island in the Black Sea in a strategic Ukrainian victory. Initially, Russia’s Ministry of Defense said it had decided to withdraw as a “goodwill gesture” to open a humanitarian corridor. But Ukraine said it pulled out Russian forces after a massive artillery and attack on the night of 29 June.
source: Noticias
[author_name]